ODUNGE STANS
Dec 12, 2024
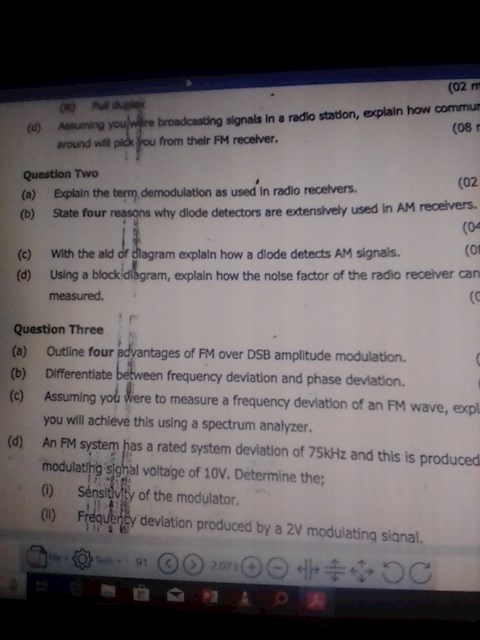
With the aid of a diagram explain how a diode detects AM signal.
1 view
1 view
1 answer
Sort By

Google Gemini AI
Dec 12, 2024
Diagram of a Diode Detecting an AM Signal:
[Image of a diode detector circuit, with a diode, resistor, and capacitor]
Components:
- Diode: Allows current to flow in only one direction.
- Resistor (R): Limits the current flowing through the diode.
- Capacitor (C): Stores the detected signal.
Operation:
1. Positive Half-Cycle:
- The positive peak of the AM signal causes the diode to conduct.
- Current flows through the diode and charges the capacitor.
- The voltage across the capacitor increases, proportional to the amplitude of the AM signal.
2. Negative Half-Cycle:
- The negative peak of the AM signal causes the diode to reverse-bias, preventing current flow.
- The capacitor discharges through the resistor, slowly releasing its stored energy.
- The voltage across the capacitor decreases, tracking the envelope of the AM signal.
3. Smoothing:
- The resistor and capacitor form a low-pass filter that smooths out the voltage fluctuations across the capacitor.
- This filtered signal represents the amplitude of the original AM signal, which can be used to recreate the audio content.
Output:
- The voltage across the capacitor represents the demodulated AM signal.
- This signal can be amplified and played through a speaker or headphones.
[Image of a diode detector circuit, with a diode, resistor, and capacitor]
Components:
- Diode: Allows current to flow in only one direction.
- Resistor (R): Limits the current flowing through the diode.
- Capacitor (C): Stores the detected signal.
Operation:
1. Positive Half-Cycle:
- The positive peak of the AM signal causes the diode to conduct.
- Current flows through the diode and charges the capacitor.
- The voltage across the capacitor increases, proportional to the amplitude of the AM signal.
2. Negative Half-Cycle:
- The negative peak of the AM signal causes the diode to reverse-bias, preventing current flow.
- The capacitor discharges through the resistor, slowly releasing its stored energy.
- The voltage across the capacitor decreases, tracking the envelope of the AM signal.
3. Smoothing:
- The resistor and capacitor form a low-pass filter that smooths out the voltage fluctuations across the capacitor.
- This filtered signal represents the amplitude of the original AM signal, which can be used to recreate the audio content.
Output:
- The voltage across the capacitor represents the demodulated AM signal.
- This signal can be amplified and played through a speaker or headphones.
0