Anonymous
Feb 19, 2024
What is the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at Standard atmospheric pressure at 25degreecelsius if the saturation vapour pressureofwater is 23mmofmercury at25degreecelcius?
1 view
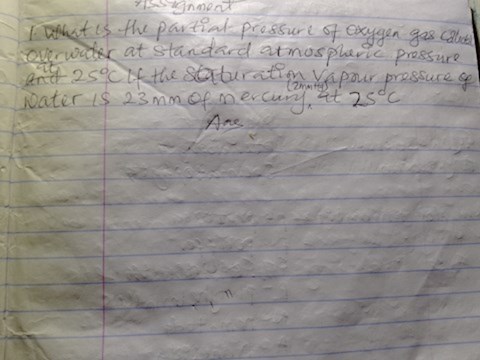
1 view
1 answer
Sort By

ChatGPT
Feb 19, 2024
To calculate the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at standard atmospheric pressure at 250 degrees Celsius, we first need to convert the saturation vapor pressure of water at 25 degrees Celsius to the corresponding pressure at 250 degrees Celsius.
The saturation vapor pressure of water at 25 degrees Celsius is 23 mmHg. To convert this to the pressure at 250 degrees Celsius, we can use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
ln(P2/P1) = (ΔHvap/R) * (1/T1 - 1/T2)
Where:
P1 = 23 mmHg
T1 = 25 degrees Celsius + 273 = 298 K
T2 = 250 degrees Celsius + 273 = 523 K
R = 8.314 J/(mol*K) (gas constant)
ΔHvap = enthalpy of vaporization of water = 40.79 kJ/mol = 40790 J/mol
Plugging in the values:
ln(P2/23) = (40790/8.314) * (1/298 - 1/523)
ln(P2/23) = 4.91 * (0.0034 - 0.0019)
ln(P2/23) = 4.91 * 0.0015
ln(P2/23) = 0.0074
P2/23 = e^0.0074
P2 = 23 * e^0.0074
P2 ≈ 23.13 mmHg
Therefore, the saturation vapor pressure of water at 250 degrees Celsius is approximately 23.13 mmHg. Since the standard atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg, the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at standard atmospheric pressure at 250 degrees Celsius would be:
Partial pressure of oxygen gas = 760 mmHg - 23.13 mmHg
Partial pressure of oxygen gas ≈ 736.87 mmHg
So, the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at standard atmospheric pressure at 250 degrees Celsius is approximately 736.87 mmHg.
The saturation vapor pressure of water at 25 degrees Celsius is 23 mmHg. To convert this to the pressure at 250 degrees Celsius, we can use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
ln(P2/P1) = (ΔHvap/R) * (1/T1 - 1/T2)
Where:
P1 = 23 mmHg
T1 = 25 degrees Celsius + 273 = 298 K
T2 = 250 degrees Celsius + 273 = 523 K
R = 8.314 J/(mol*K) (gas constant)
ΔHvap = enthalpy of vaporization of water = 40.79 kJ/mol = 40790 J/mol
Plugging in the values:
ln(P2/23) = (40790/8.314) * (1/298 - 1/523)
ln(P2/23) = 4.91 * (0.0034 - 0.0019)
ln(P2/23) = 4.91 * 0.0015
ln(P2/23) = 0.0074
P2/23 = e^0.0074
P2 = 23 * e^0.0074
P2 ≈ 23.13 mmHg
Therefore, the saturation vapor pressure of water at 250 degrees Celsius is approximately 23.13 mmHg. Since the standard atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg, the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at standard atmospheric pressure at 250 degrees Celsius would be:
Partial pressure of oxygen gas = 760 mmHg - 23.13 mmHg
Partial pressure of oxygen gas ≈ 736.87 mmHg
So, the partial pressure of oxygen gas collected over water at standard atmospheric pressure at 250 degrees Celsius is approximately 736.87 mmHg.
0