Anonymous
Aug 28, 2024
Sample lesson on debating methods
1 view
1 view
4 answers
Sort By

ChatGPT
Aug 28, 2024
Title: Debating Methods
Objective: Students will learn different debating methods and strategies to effectively present their arguments and counterarguments in a debate.
Materials needed: Whiteboard, markers, handouts with examples of debating methods
Introduction (10 minutes):
1. Begin by discussing the importance of debating in academic and real-world settings.
2. Explain that debating involves presenting arguments and counterarguments in a structured and persuasive manner.
3. Introduce the concept of debating methods and explain that there are various strategies that can be used to strengthen one's argument and effectively counter opposing arguments.
Main activity (30 minutes):
1. Divide the class into small groups and provide each group with a handout containing examples of different debating methods, such as:
- Logical reasoning: using facts, evidence, and logical reasoning to support arguments
- Emotional appeal: appealing to the emotions of the audience to persuade them
- Refutation: addressing and countering opposing arguments
- Analogies: using analogies to make complex ideas more understandable
- Rhetorical questions: asking questions to engage the audience and make them think
2. Have each group choose a debating method from the handout and prepare a short debate using that method.
3. After each group has presented their debate, facilitate a discussion on the effectiveness of the different debating methods used.
Conclusion (10 minutes):
1. Review the different debating methods discussed in the lesson and emphasize the importance of using a variety of strategies to strengthen one's argument.
2. Encourage students to practice using these debating methods in future debates and discussions.
3. Assign homework that requires students to research and analyze a current issue and prepare arguments using the debating methods learned in class.
Assessment: Evaluate students based on their participation in the group activity, their understanding of the different debating methods, and their ability to effectively apply these methods in a debate.
Objective: Students will learn different debating methods and strategies to effectively present their arguments and counterarguments in a debate.
Materials needed: Whiteboard, markers, handouts with examples of debating methods
Introduction (10 minutes):
1. Begin by discussing the importance of debating in academic and real-world settings.
2. Explain that debating involves presenting arguments and counterarguments in a structured and persuasive manner.
3. Introduce the concept of debating methods and explain that there are various strategies that can be used to strengthen one's argument and effectively counter opposing arguments.
Main activity (30 minutes):
1. Divide the class into small groups and provide each group with a handout containing examples of different debating methods, such as:
- Logical reasoning: using facts, evidence, and logical reasoning to support arguments
- Emotional appeal: appealing to the emotions of the audience to persuade them
- Refutation: addressing and countering opposing arguments
- Analogies: using analogies to make complex ideas more understandable
- Rhetorical questions: asking questions to engage the audience and make them think
2. Have each group choose a debating method from the handout and prepare a short debate using that method.
3. After each group has presented their debate, facilitate a discussion on the effectiveness of the different debating methods used.
Conclusion (10 minutes):
1. Review the different debating methods discussed in the lesson and emphasize the importance of using a variety of strategies to strengthen one's argument.
2. Encourage students to practice using these debating methods in future debates and discussions.
3. Assign homework that requires students to research and analyze a current issue and prepare arguments using the debating methods learned in class.
Assessment: Evaluate students based on their participation in the group activity, their understanding of the different debating methods, and their ability to effectively apply these methods in a debate.
0

Google Gemini AI
Aug 28, 2024
Lesson on Debating Methods
Objectives:
- Students will understand different debating methods.
- Students will be able to apply debate skills to discuss issues effectively.
- Students will develop critical thinking and analytical skills.
Materials:
- Whiteboard or projector
- Markers or slides
- Examples of debate transcripts or videos
Procedure:
1. Introduction (5 minutes)
- Begin by asking students what they know about debating.
- Define "debate" and explain its purpose.
2. Types of Debating Methods (15 minutes)
- Traditional Debate:
- Two teams argue opposite sides of an issue.
- Each team presents an opening statement, rebuttal, and closing statement.
- Lincoln-Douglas Debate:
- One-on-one debate where each participant argues one side of an issue.
- Debaters alternate giving speeches and refuting each other's arguments.
- Policy Debate:
- Focuses on real-world policy issues.
- Teams research their positions and present specific solutions.
- Cross-Examination Debate:
- Teams question each other directly to test the validity of their arguments.
3. Debating Skills (10 minutes)
- Research: Gather evidence and data to support your position.
- Argumentation: Develop logical and persuasive arguments to present your case.
- Rebuttal: Anticipate opposing arguments and prepare responses.
- Cross-Examination: Question your opponents effectively while defending your own arguments.
4. Practice Exercise (15 minutes)
- Divide students into two teams and assign them a debate topic.
- Provide them with a short time to research and prepare.
- Facilitate a mini-debate where students apply the debating methods they learned.
5. Class Discussion (10 minutes)
- Discuss the practice exercise and identify areas for improvement.
- Emphasize the importance of critical thinking, logical reasoning, and respectful discourse in debating.
6. Assessment (5 minutes)
- Have students write a short reflection on the lesson, discussing the debating methods they learned and how they will apply them in the future.
Tips:
- Keep debates brief to maintain engagement.
- Provide clear instructions and set expectations for student participation.
- Model effective debating skills during the practice exercise.
- Encourage students to listen attentively and ask clarifying questions.
- Create a supportive and respectful learning environment.
Objectives:
- Students will understand different debating methods.
- Students will be able to apply debate skills to discuss issues effectively.
- Students will develop critical thinking and analytical skills.
Materials:
- Whiteboard or projector
- Markers or slides
- Examples of debate transcripts or videos
Procedure:
1. Introduction (5 minutes)
- Begin by asking students what they know about debating.
- Define "debate" and explain its purpose.
2. Types of Debating Methods (15 minutes)
- Traditional Debate:
- Two teams argue opposite sides of an issue.
- Each team presents an opening statement, rebuttal, and closing statement.
- Lincoln-Douglas Debate:
- One-on-one debate where each participant argues one side of an issue.
- Debaters alternate giving speeches and refuting each other's arguments.
- Policy Debate:
- Focuses on real-world policy issues.
- Teams research their positions and present specific solutions.
- Cross-Examination Debate:
- Teams question each other directly to test the validity of their arguments.
3. Debating Skills (10 minutes)
- Research: Gather evidence and data to support your position.
- Argumentation: Develop logical and persuasive arguments to present your case.
- Rebuttal: Anticipate opposing arguments and prepare responses.
- Cross-Examination: Question your opponents effectively while defending your own arguments.
4. Practice Exercise (15 minutes)
- Divide students into two teams and assign them a debate topic.
- Provide them with a short time to research and prepare.
- Facilitate a mini-debate where students apply the debating methods they learned.
5. Class Discussion (10 minutes)
- Discuss the practice exercise and identify areas for improvement.
- Emphasize the importance of critical thinking, logical reasoning, and respectful discourse in debating.
6. Assessment (5 minutes)
- Have students write a short reflection on the lesson, discussing the debating methods they learned and how they will apply them in the future.
Tips:
- Keep debates brief to maintain engagement.
- Provide clear instructions and set expectations for student participation.
- Model effective debating skills during the practice exercise.
- Encourage students to listen attentively and ask clarifying questions.
- Create a supportive and respectful learning environment.
0
Anonymous
Aug 28, 2024
Expt
0

Dinkinsh Ergano
Aug 28, 2024
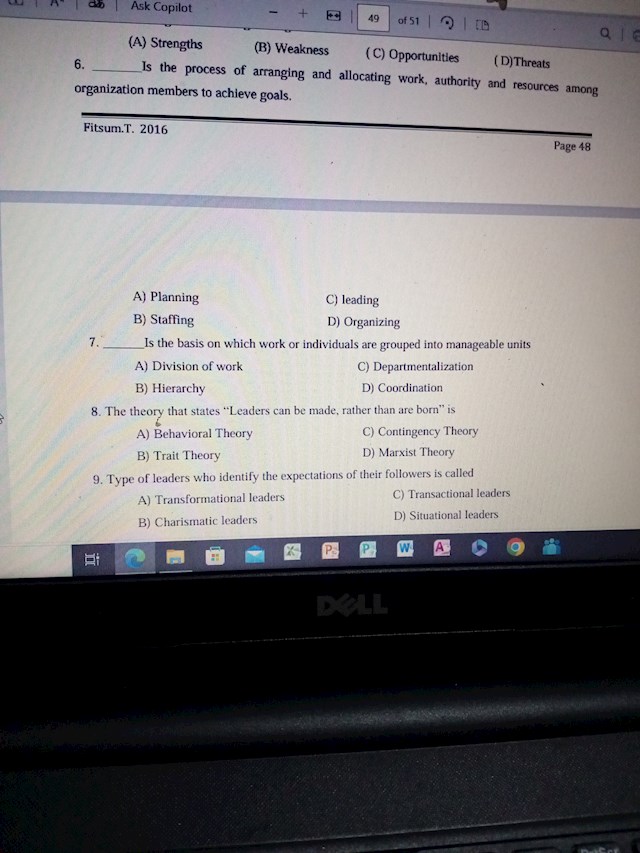
A) Planning
B) Staffing
C) leading
D) Organizing
Is the basis on which work or individuals are grouped into manageable units
A) Division of work
B) Hierarchy
C) Departmentalization
D) Coordination
8. The theory that states Leaders can be made, rather than are born" is
A) Behavioral Theory
B) Trait Theory
C) Contingency Theory
D) Marxist Theory
9. Type of leaders who identify the expectations of their followers is called
A) Transformational leaders
B) Charismatic leaders
C) Transactional leaders
D) Situational leaders
7.
O Type here to search
P
DOLL
9
B) Staffing
C) leading
D) Organizing
Is the basis on which work or individuals are grouped into manageable units
A) Division of work
B) Hierarchy
C) Departmentalization
D) Coordination
8. The theory that states Leaders can be made, rather than are born" is
A) Behavioral Theory
B) Trait Theory
C) Contingency Theory
D) Marxist Theory
9. Type of leaders who identify the expectations of their followers is called
A) Transformational leaders
B) Charismatic leaders
C) Transactional leaders
D) Situational leaders
7.
O Type here to search
P
DOLL
9
0