Anonymous
Oct 29, 2023
Please?
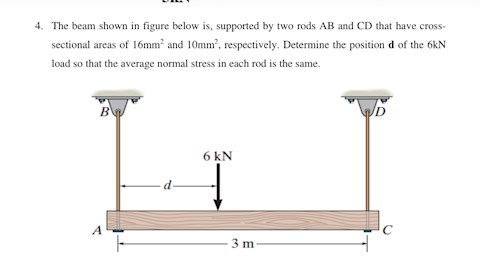
The beam shown in figure below is, supported by two rods AB and CD that have cross-sectional areas of 16mm^2 and 10mm^2, respectively. Determine the position d of the 6kN load so that the average normal stress in each rod is the same
1 view
1 view
1 answer
Sort By

ChatGPT
Oct 29, 2023
To determine the position d of the 6kN load so that the average normal stress in each rod is the same, we need to consider the equilibrium of forces and the stress in each rod.
Let's denote the distance from point A to the load as x, and the distance from the load to point D as d - x.
First, let's calculate the stress in rod AB. The stress in a rod is given by the formula:
Stress = Force / Area
The force in rod AB is equal to the 6kN load, and the area is 16mm^2. Therefore, the stress in rod AB is:
Stress_AB = 6kN / 16mm^2
Next, let's calculate the stress in rod CD. The force in rod CD is also equal to the 6kN load, and the area is 10mm^2. Therefore, the stress in rod CD is:
Stress_CD = 6kN / 10mm^2
Since we want the average normal stress in each rod to be the same, we can set the two stresses equal to each other:
Stress_AB = Stress_CD
6kN / 16mm^2 = 6kN / 10mm^2
To simplify the equation, we can cancel out the kN units:
6 / 16 = 6 / 10
Cross-multiplying, we get:
10 * 6 = 16 * 6
60 = 96
This equation is not true, which means there is no position d that will make the average normal stress in each rod the same.
Let's denote the distance from point A to the load as x, and the distance from the load to point D as d - x.
First, let's calculate the stress in rod AB. The stress in a rod is given by the formula:
Stress = Force / Area
The force in rod AB is equal to the 6kN load, and the area is 16mm^2. Therefore, the stress in rod AB is:
Stress_AB = 6kN / 16mm^2
Next, let's calculate the stress in rod CD. The force in rod CD is also equal to the 6kN load, and the area is 10mm^2. Therefore, the stress in rod CD is:
Stress_CD = 6kN / 10mm^2
Since we want the average normal stress in each rod to be the same, we can set the two stresses equal to each other:
Stress_AB = Stress_CD
6kN / 16mm^2 = 6kN / 10mm^2
To simplify the equation, we can cancel out the kN units:
6 / 16 = 6 / 10
Cross-multiplying, we get:
10 * 6 = 16 * 6
60 = 96
This equation is not true, which means there is no position d that will make the average normal stress in each rod the same.
1